In today’s self-care-driven world, beauty salons and medical spas have become go-to destinations for people looking to enhance their appearance, boost their confidence, and enjoy a little well-deserved pampering. From a quick haircut at your favorite beauty salon to a transformative anti-aging treatment at a medical spa, the options for personal care have never been broader or more advanced.
However, with so many overlapping services—like facials, skin treatments, and body care—many people struggle to understand the difference between a medical spa and salon. Both settings can feel relaxing, luxurious, and inviting, but the expertise, equipment, and results can vary significantly. This confusion often leads to uncertainty about where to book an appointment for specific goals, whether it’s a soothing massage, wrinkle reduction, or advanced skin rejuvenation.

What Is a Salon?
Defining a Beauty Salon
A beauty salon is a professional space dedicated to enhancing a client’s appearance through hair, skin, nail, and cosmetic treatments. When you think of what a salon is, imagine a welcoming, stylish environment where skilled professionals focus on helping you look and feel your best.
Unlike medical spas, salons do not perform procedures that require medical oversight. Instead, they offer beauty-focused treatments designed to refresh your style, boost your confidence, and provide a relaxing escape from everyday stress. Many beauty salons also offer esthetician services such as basic facials and skin care routines, ensuring that your visit is both pampering and results-driven. The emphasis is on enjoyment and immediate, visible beauty enhancements rather than medical-grade corrective treatments.

Common Salon Services
Beauty salons provide a wide range of services that cater to everyday grooming and aesthetic needs. Hair services often include cutting, styling, coloring, highlights, and special occasion updos. Nail care options range from classic manicures and pedicures to gel applications and intricate nail art. Many salons also offer waxing for smooth, hair-free skin, along with lash extensions and brow shaping to frame the face beautifully.
For skin care, esthetician services typically include basic facials, exfoliation, and hydration treatments using spa-grade—not medical-grade—products. Some beauty salons also incorporate makeup application, spray tanning, and scalp treatments into their menu. While the focus is primarily on short-term beauty results and relaxation, the experience of a beauty salon visit is just as important as the service itself—providing clients with a comfortable, feel-good atmosphere where self-care is celebrated.
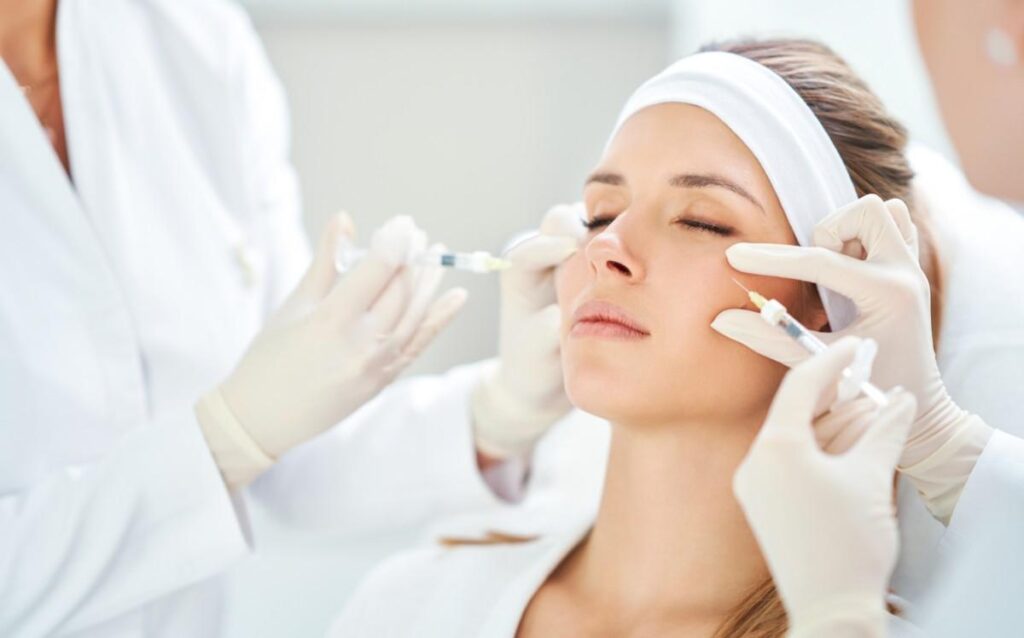
What Is a Medical Spa?
Defining a Medical Spa
A medical spa, often called a “med spa,” is a hybrid between a traditional spa and a medical clinic. What is a medical spa exactly? In simple terms, it’s a place where the relaxation and ambiance of a beauty spa meet the advanced treatments and professional oversight of licensed medical staff. The medical spa’s meaning centers on providing aesthetic and skin health services that go beyond surface-level beauty, delivering deeper, often longer-lasting results.
Unlike salons or regular day spas, medical spa services are administered or supervised by qualified medical professionals such as physicians, nurse practitioners, or physician assistants. This allows them to offer advanced skin rejuvenation, corrective treatments, and specialized care for various conditions. While you’ll still find a calm, welcoming environment, a medical spa’s focus is on combining comfort with clinical precision, giving clients the benefits of both pampering and professional-grade outcomes.

Common Medical Spa Services
The range of medical spa services is broader and more advanced than those offered at a traditional salon. Common treatments include Botox and other neuromodulators to smooth fine lines and wrinkles, as well as dermal fillers to restore lost volume and enhance facial contours. Many medical spa variations also feature laser hair removal for permanent hair reduction, chemical peels to address hyperpigmentation and texture issues, and microdermabrasion for deep exfoliation and skin renewal.
Advanced technologies like radiofrequency skin tightening, non-surgical body contouring (e.g., CoolSculpting), and microneedling can target stubborn fat, sagging skin, or acne scars. Some med spas offer innovative scalp health treatments like Hydrafacial to promote thicker, healthier hair. Unlike standard facials at a salon, these treatments often aim for corrective, restorative, or preventative results—helping repair sun damage, slow signs of aging, and improve skin health over time.
The combination of cutting-edge technology, medical oversight, and a spa-like atmosphere makes the medical spa an ideal choice for those seeking visible, lasting improvements.
Medical Spa vs Salon — Key Differences
Services Offered
When exploring the difference between a medical spa and salon, the most obvious distinction is in the type of services provided. A beauty salon focuses on surface-level beauty enhancements such as haircuts, coloring, manicures, pedicures, waxing, lash extensions, and basic facials. These treatments aim to refresh your look, maintain grooming, and provide a pleasant, pampering experience.
In contrast, a medical spa offers medically supervised treatments that address deeper skin and body concerns. This may include Botox, dermal fillers, laser treatments, chemical peels, microneedling, and body contouring procedures. These services go beyond cosmetic upkeep—they are designed to repair skin damage, reverse signs of aging, and promote long-term skin health. The difference between medical spa and salon becomes clear when you consider that med spa procedures often require specialized technology and clinical expertise for safe and effective results.
Staff Qualifications
Another defining factor in the medical spa vs salon discussion is the qualifications of the professionals providing the services. In a salon, treatments are typically performed by licensed cosmetologists or estheticians who are trained in hair, skin, and nail care. While they are highly skilled in their craft, they do not perform medical-grade procedures.
In a medical spa, however, treatments are administered or overseen by licensed medical professionals such as physicians, nurse practitioners, or physician assistants. This medical oversight ensures that advanced procedures are performed safely, tailored to the client’s unique skin needs, and backed by clinical expertise.
Treatment Goals
The difference between a medical spa and salon also extends to the end results they aim to achieve. Salons focus on immediate, visible beauty and relaxation—offering services that make you feel refreshed for a special occasion or everyday confidence. Medical spas, on the other hand, prioritize corrective, restorative, and preventative care, with results that often last longer and address underlying issues. In short, when deciding what is the difference between the two, it comes down to short-term cosmetic enhancement versus long-term aesthetic and medical improvement.

How to Choose Between a Medical Spa and Salon
When deciding between a salon and a medical spa, your choice should be guided by your personal goals, the level of treatment you require, and the results you expect. While both offer a relaxing, client-focused experience, they cater to different needs and outcomes. Understanding these differences will help you make an informed decision that ensures your time, money, and expectations are well-matched to the service provider.
Choosing a Salon
A beauty salon is ideal if your main priority is routine beauty maintenance or a quick confidence boost. Salons are perfect for haircuts, coloring, styling, manicures, pedicures, and basic aesthetician services such as hydrating facials or gentle exfoliation. They excel at creating a fresh, polished look for special occasions or everyday wear, all in a comfortable and pampering environment. If you want to enjoy regular self-care without the need for medical oversight, a salon is your go-to destination.
Choosing a Medical Spa
A medical spa is the better choice if you’re seeking targeted skin rejuvenation, anti-aging treatments, or corrective procedures that go beyond the surface. Whether you’re addressing fine lines, sun damage, acne scars, or volume loss, medical spa services—such as Botox, dermal fillers, laser treatments, and advanced facials—are performed with medical supervision for safety and precision. If your goal is to achieve longer-lasting, corrective results with the latest aesthetic technology, a medical spa provides the expertise and advanced treatments needed to reach those outcomes.
Conclusion — The Right Choice for Your Beauty Goals
When it comes to enhancing your appearance and practicing self-care, both beauty salons and medical spas have their own unique strengths. A beauty salon offers the comfort of familiar aesthetician services, hair care, nail treatments, and everyday pampering—perfect for maintaining your style and enjoying regular moments of relaxation. On the other hand, a medical spa provides advanced, medically supervised treatments designed to correct, restore, and rejuvenate your skin and body with longer-lasting results.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to what is the difference that matters most to you. If you’re seeking a quick refresh, a confidence boost for an event, or routine grooming, a salon is your best choice. But if you have specific aesthetic concerns—such as fine lines, sun damage, uneven skin tone, or stubborn fat—a medical spa offers the expertise, technology, and precision to address them safely and effectively.
By understanding the difference between a medical spa and salon, you can make informed choices that align with your beauty goals, budget, and comfort level. Whether you choose a beauty salon, a medical spa, or a mix of both, the most important thing is finding a trusted provider who understands your needs and helps you look and feel your absolute best.
FAQs — Answering Common Questions
- What is the difference between a medical spa and salon?
The main difference between a medical spa and salon lies in the type of services offered and the qualifications of the staff. Salons focus on beauty maintenance such as haircuts, coloring, nail care, and basic facials, while medical spas provide advanced treatments like Botox, dermal fillers, and laser therapies under medical supervision.
- Are Aesthetician services available at both a beauty salon and a medical spa?
Yes, both beauty salons and medical spas may offer esthetician services such as facials and skin care. However, med spa estheticians often work alongside medical professionals to perform more advanced treatments.
- Can I get Botox at a beauty salon?
No, Botox can only be administered in a setting with medical oversight because it is a prescription treatment that requires professional training and certification.
- Which is better for anti-aging — a medical spa or salon?
For anti-aging, a medical spa is the better choice. Medical spa services target deeper skin layers and use medical-grade treatments to reduce wrinkles, restore volume, and improve skin texture for long-lasting results.
- Are there medical spa variations for different needs and budgets?
Yes, many medical spas offer different packages and service tiers to accommodate varying skin concerns, goals, and budgets—ranging from single-session treatments to ongoing care plans.
- How often should I visit a medical spa compared to a salon?
Salon visits are typically more frequent—every few weeks for hair or nail maintenance—while medical spa visits depend on your treatment plan. Some clients go every few months for touch-ups or seasonal treatments.
The post What is the difference between a Medical spa and Salon? appeared first on Spa in the City.
source https://spainthecitydallas.com/what-is-the-difference-between-a-medical-spa-and-salon/




